


When noise irritates you, it can cause physical and psychological discomfort, stress, and distraction. The degree of irritation can vary depending on the type, intensity, duration, and frequency of the noise, as well as individual factors such as personality, mood, and sensitivity to sound.
Feeling agitated, frustrated, or impatient due to the noise.
Having difficulty focusing, concentrating, or completing tasks due to noise.
Feeling tense, anxious, or overwhelmed due to the noise.
Having difficulty falling or staying asleep due to the noise.
Experiencing physical discomforts, such as headaches, nausea, or muscle tension due to the noise.
To avoid or reduce noise irritation, it is important to identify the sources of noise. As to minimize exposure to them. And to use protective measures such as earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones. Additionally, creating a quiet and peaceful environment, practicing relaxation techniques, and engaging in stress-reducing activities can help alleviate the negative effects of noise on your well-being.

Various human activities cause noise pollution. This can result in discomfort experienced by humans especially small children and the elderly and animals. Some common sources of noise pollution include:
C&D activities, industrial processes, loud machinery processes, etc. can generate noise. Moreover, excessive noise from industrial processes can reduce productivity and increase worker safety risks.
Loud music, fireworks, etc. can cause an excessive amount of noise. Long-term exposure to loud noise from recreational activities can also cause hearing loss and other related health problems.
Increased urbanization, including the construction of buildings and roads, can lead to increased noise pollution. Noise pollution in urban areas can also have an impact on wildlife. As by changing their behaviour and communication patterns.
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, volcanic eruptions, tornadoes, and thunderstorms can also cause noise pollution. As through the sound of strong winds, thunder, and other related sounds.
Various household activities such as vacuum cleaning, blenders, and certain household appliances can generate noise. Noise can be annoying to family members, neighbours, and even pets, resulting in increased stress.
To mitigate the negative effects of noise pollution, various strategies have been used. As by including noise barriers, soundproofing, and regulations to limit noise levels from various sources.
Noise levels in sleeping areas should be kept below 35 dB(A).
The Noise levels in living areas should be kept below 45 dB(A).
Noise levels in work areas should be kept below 55 dB(A).
Humans can typically hear sounds between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz, but some animals can hear sounds at much higher or lower frequencies. For example, dogs can hear frequencies up to 65,000 Hz, while whales can communicate with sounds at frequencies as low as 10 Hz.
High noise levels can cause various negative effects on humans, animals, wildlife, and the overall ecosystem. Noise in excessive levels can cause:
Prolonged exposure to excessive noise can cause stress and anxiety, leading to physical and mental health problems.
Excessive noise can make it difficult to communicate, leading to social and psychological problems.
Exposure to high levels of noise can damage the cells in the inner ear, which can lead to hearing loss and deafness.
Prolonged exposure to excessive noise can cause trouble in sleeping which leads to insomnia and sleep disturbances.
Excessive noise can cause hypertension and various cardiovascular problems, especially in older people.
High levels of noise can cause disturbances among wildlife. This includes disturbance in mating calls, breeding patterns, etc.
affects the environment?
Noise pollution can have negative effects on the environment, including wildlife and ecosystems. Some of these negative effects include:
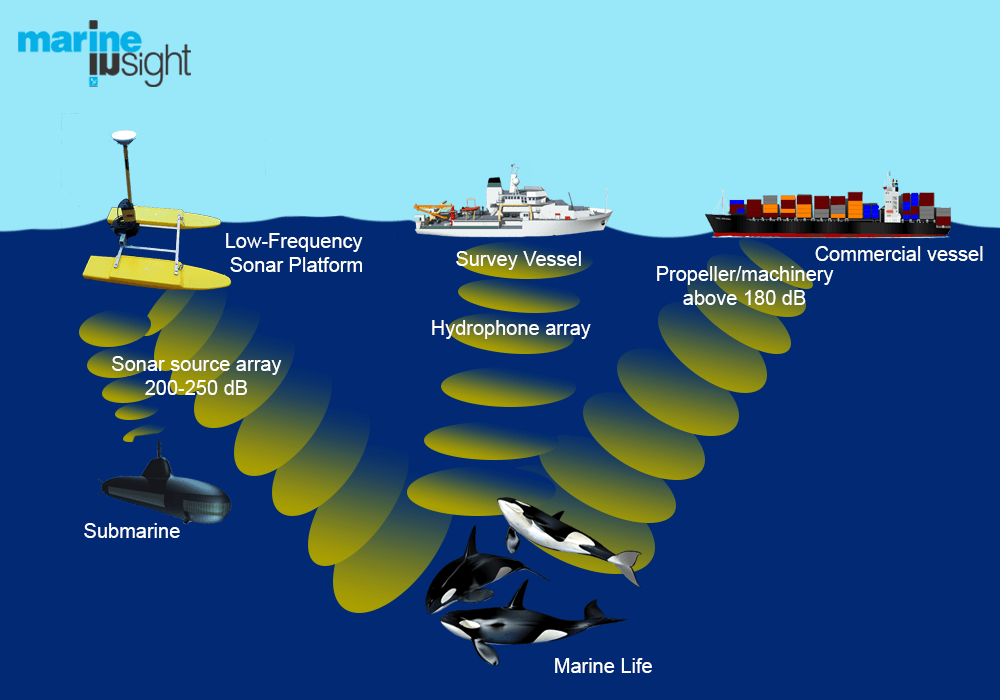
Noise pollution can alter the composition of animal communities. As some species are more sensitive to noise than others.
Noise pollution can cause animals to avoid certain areas. It can lead to habitat loss and fragmentation.
Excessive noise can affect the growth and development of plants. It leads to the changes in the structure of ecosystems.
The negative effects of noise pollution on animals and plants can lead to imbalances in ecosystems.
According to a study conducted by experts at California Polytechnic State University, human noise pollution has an impact on the diversity of plant life in an environment even after the noise is eliminated.
It's important to note that these effects can vary depending on factors such as duration of exposure, frequency of exposure, and individual susceptibility to noise. Therefore, it's crucial to take steps to reduce noise pollution whenever possible, regardless of the noise level.
| Noise Levels | Indoor | Outdoor |
|---|---|---|
| 50-60 dB | Normal conversation | Quiet suburb or light traffic on a highway |
| 50-60 dB | Background music at a low volume | Normal conversation or a busy street |
| 70-80 dB | Busy street noise heard from indoors | Traffic noise or a motorcycle passing by |
| 70-75 dB | Vacuum cleaner | Noisy restaurant kitchen or a jackhammer |
| 85-100 dB | Loud music from speakers | Concert music or a car horn |
| 90-120 dB | Power tools | Thunder or a jet plane taking off |
Noise Level
50-60 dB
Indoor
Normal conversation
Outdoor
Quiet suburb or light traffic on a highway
Noise Level
50-60 dB
Indoor
Background music at a low volume
Outdoor
Normal conversation or a busy street
Noise Level
70-80 dB
Indoor
Busy street noise heard from indoors
Outdoor
Traffic noise or a motorcycle passing by
Noise Level
70-75 dB
Indoor
Vacuum cleaner
Outdoor
Noisy restaurant kitchen or a jackhammer
Noise Level
85-100 dB
Indoor
Loud music from speakers
Outdoor
Concert music or a car horn
Noise Level
90-120 dB
Indoor
Power tools
Outdoor
Thunder or a jet plane taking off
Noise pollution can have negative effects on the environment, including wildlife and ecosystems. Some of these negative effects include:
Noise barriers can be used to reduce noise pollution from highways, railways, and other sources.
Trees and vegetation can help absorb sound waves, reducing the amount of noise that reaches people.
Governments can enforce regulations and standards for noise levels, which can include limits on noise emissions from various sources, and can require noise-reducing technologies to be used.
Insulating buildings can reduce the amount of noise that enters them. This can be done by using double-glazed windows, soundproof curtains, and acoustic panels.
Educating people about the negative impacts of noise pollution and the ways to control it can be an effective way to raise awareness and encourage action. Overall, controlling noise pollution requires a combination of efforts from individuals, businesses, and governments.